Soft Robotics Revolution : Silicone, 3D Printing, and Use Cases
Lynxter was one of the few to explore how additive manufacturing was serving soft robotics projects, particularly through an innovative collaboration with Schneider Electric. In this article, we will dive into the transformative impact of silicone 3D printing on the field of soft robotics, examining its applications, and the groundbreaking possibilities it introduces to redefine contemporary approaches to production and healthcare.
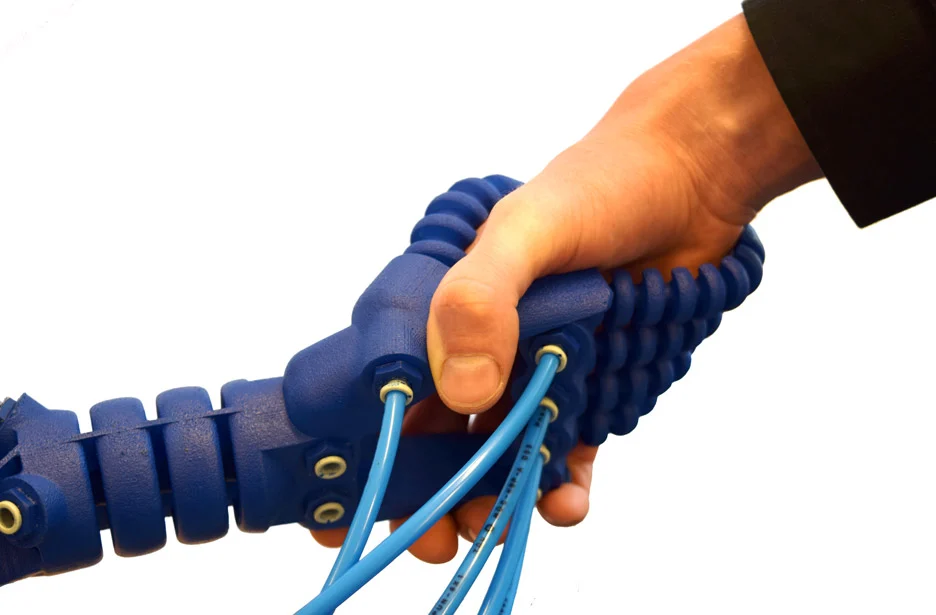
The S300X LIQ 21 | LIQ11 3D Printer print soft robotic gripper
Silicone, the foundation of soft robotics
Silicone materials have emerged as key components in the realm of soft robotics, offering a combination of flexibility, biocompatibility, and durability. Their inherent softness allows for intricate and adaptable movements, mirroring the suppleness of natural tissues. This characteristic flexibility is particularly advantageous in soft robotics, enabling machines to navigate complex environments and interact with delicate objects without causing damage. The material’s durability enhances as well its suitability for prolonged use, showcasing resistance to wear and tear over time.
Silicone’s amazing flexibility in soft robotics not only highlights its importance in engineering but also opens the door to creative solutions in healthcare and other areas. For example, silicone’s biocompatibility makes it an ideal choice for applications in medical devices and prosthetics, ensuring minimal risk of adverse reactions when integrated with the human body.
Details of a soft robotics gripper’s finger on the S300X LIQ21 | LIQ11 3D Printer
Example of 3D printed gripper’s finger with and without air injection.
Manufacturing and Industry 4.0 advancement
Silicone and 3D printing have become dynamic catalysts in reshaping modern manufacturing processes, and is today revolutionizing the landscape of collaborative robots and automation.
In electronics manufacturing, delicate components such as microchips and sensors require precise handling during assembly. Traditional rigid robotic grippers may damage these components or struggle to grip them securely. Same things happen in the food industry, handling soft and irregularly shaped objects such as fruits and vegetables, poses challenges for traditional robotic pick-and-place systems.
Delicate product like potatoes chips can be securely handled with soft robotics grippers.
A viable solution comes in the form of soft robotic pneumatic or hydraulic grippers equipped with compliant materials. They are designed to adapt seamlessly to the intricate shapes of delicate components. As mentioned, these grippers utilize pneumatic or hydraulic systems to provide controlled and gentle grasping. The compliance of the gripper allows it to conform to the irregular shapes of any components, ensuring a secure hold without causing deterioration. This integration is particularly beneficial for industries requiring delicate handling, such as food industry, textile and apparel, pharmaceuticals for sensitive medicines and medical devices, or optical manufacturing, to name a few examples.
This synergy offers a flexible and responsive manufacturing environment, where robots can adapt swiftly to changing production needs. Such innovations are not only streamlining operations but also contributing to safer and more collaborative workplaces.
Soft Robotics for healthcare innovations
Silicone-based soft robotics are exerting a transformative influence on healthcare applications, ushering in a new era of patient-centric solutions.
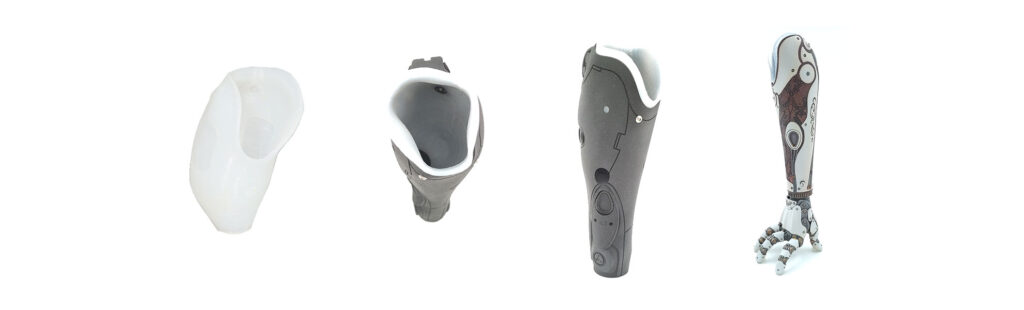
In the realm of prosthetics, 3D-printed silicone-based soft robotic limbs offer unparalleled adaptability, mimicking natural movements can significantly improve the quality of life for amputees. The marriage of silicone and 3D printing extends to personalized medical devices. This not only enhances the effectiveness of treatment but also ensures a higher level of patient comfort.
Additionally, there has been notable progress in exploring the potential use of soft robotics in minimally invasive surgeries (MIS) or Robot-assisted minimally invasive surgery (RAMIS). However, current RAMIS often meet limitations due to their rigid component design, making it difficult to reach specific areas of the body and potentially causing tissue injuries.
The flexibility in form and structure of soft robotics can offer a promising solution to these challenges, enabling the potential for conducting surgical procedures with enhanced precision and safety.
Soft robotics is fundamentally reshaping the landscape of patient care by providing more tailored and efficient solutions for a wide range of medical procedures.

Soft robotics prosthetic hand prototype from Rob Scharff‘s Soft Robotics research project.
Silicone 3D printing’s impact on soft robotics
Silicone additive manufacturing plays a pivotal role in the creation of soft robotic structures, offering notable advantages such as rapid prototyping, and the ability to produce complex geometries that traditional methods often find challenging.
The iterative nature of 3D printing allows for swift refinement and modification of designs, expediting the development process of soft robotic systems. One of the key strengths lies in the ability to fabricate tailored and intricate parts (thickness and hollow spaces) that match the specific requirements of soft robots, enabling high levels of precision.
Example of 3D printed soft robotic grippers by Lynxter.
Notable examples include the development of grippers, actuators, and wearable assistive devices that leverage silicone 3D printing to achieve enhanced functionality and adaptability.
Example of 3D printed gripper with and without air injection.
The evolving synergy between silicone, 3D printing, and soft robotics promises new solutions and pushes the boundaries of what’s achievable in manufacturing, healthcare, and beyond. This transformative journey signifies a future where innovation meets practical applications, leaving a lasting impact on today’s industries.
Reach out to Lynxter for further insights into our research, soft robotics 3D printed grippers and use cases, and the impactful utilization of the S300X 3D Printer, already transforming manufacturing and research processes today.
DOWNLOAD THE WHITE PAPER
Download now “Improve your workflow with silicone 3D printing”.
Discover how this new technology can enhance your productivity and innovation.
Don’t miss this opportunity to gain a new competitive advantage.